Preventing Future Criminal Acts Describes Which Purpose of Punishment
Which allow for the death penalty due so because of murder. Unless criminal penalties serve valid purposes they impose useless costs and hardship.

Crime Prevention Criminal Justice Module 2 Key Issues 2a Detailed Explanation Of Tonry And Farrington S Typology
2 Punishment must be a sanction for an offense against a specific rule or law.

. 3 Punishment must be executed upon the specific offender who has allegedly or actually committed the crime. Deterrence is a method of punishment intended to discourage criminal behavior through the imposition of punishments. Deterrence is designed to deter those who witness infliction of pain upon the convicted from committing crimes themselves.
Article II In the present Convention genocide means any of the following acts committed with intent to destroy in whole or in part a national ethnical racial. 1 Punishment must involve pain or unpleasant consequences. This purpose is also referred to as revenge or administering ones just deserts or an eye-for-an-eye and tooth-for-a-tooth.
The goals of the federal state and specialized agencies that make up the criminal justice system are to mete out punishment that is appropriate deter future criminal acts rehabilitate criminals and help victims heal. Must be for an offense actual or supposed. Punishment purposes are positive justifying principles.
Must be of an offender actual or supposed. The Contracting Parties confirm that genocide whether committed in time of peace or in time of war is a crime under international law which they undertake to prevent and to punish. Punishment serves the purpose of retribution when it simply retaliates or gets even by inflicting pain or discomfort proportionate to the offense.
The act of correcting something. The purpose of punishment is to allocate moral blame to the offender for the crime and that his or her future conduct is not a proper concern for deciding punishment Hudson 1996. Must be work of personal agencies.
Unless criminal penalties serve valid purposes they impose useless costs and hardship. A criminals behavior is more likely to be influenced by seeing a police officer with handcuffs and a radio than by a new law increasing penalties. Theories of deterrence retribution just deserts rehabilitation and incapacitation as well as the idea of restorative justice will be considered in this chapter.
Must involve an unpleasantness to the victim. The act or process of punishing and changing the behavior of people who have committed crimes. The death penalty or capital punishment if one prefers a friendlier term is the planned killing of an individual by a government or ruling entity in response to a crime.
It is considered the just punishment for a person legally convicted of an action which is deemed a safety threat to society. The justice system includes every aspect of a crime including corrections. It is meant to scare warn and persuade you to choose a different path.
While specific deterrence is tailored to the individual who committed a crime general deterrence is intended to make the public at large and would-be criminals think twice about breaking the law. Deterrence theory suggests that threats of punishment or actually experiencing punishment should reduce the likelihood of reoffending. Must not be the natural consequence of an action.
22 The beneficial effects of punishment are usually said to include the recognition that the victim has suffered an unjust act and that what has occurred is neither a mere accident the product of bad luck nor the. Criminal penalties to prevent or lessen the seriousness of future criminal acts by the offender being sentenced andor by other would-be offenders. For the most part punishment serves this purpose well.
Punishment limitations are negative restraining principles. Deterrence punishments are meant to discourage someone from committing crimes. The effects of punishment and sentencing The four fundamental philosophies surrounding the purpose of sentencing are.
The act of making something such as an error or a bad condition accurate or better. The most extreme form of incapacitating punishment is the death penalty but there are several other forms including imprisonment curfews house arrest electronic monitoring and disqualification from driving for drunken drivers. Rehabilitation as Prevention Rehabilitation is preventing crime by changing the personality of the offender so that he will conform to the dictate of law Herbert Packer Medical Model of Criminal Law - crime is disease offenders are sick Purpose of punishment is to treat criminals Incarceration as rehabilitation length depends on how long it takes to cure the offender.
Even when the purposes are valid punishment may be limited by moral values or practical concerns. Therefore it is a moral action against criminals famously advanced by Jeremy Bentham 1748-1832 since it produces the greatest happiness of the greatest number of people. Criminal penalties have the potential to achieve these crime-control effects through at least five causal mechanisms.
Argues punishment in sense of sanction imposed for criminal offense consists of five elements. Preventing future criminal acts describes deterrence. Punishment limitations are negative restraining principles.
A change that makes something right true accurate etc. Increasing the severity of punishment does little to deter crime. Strategies that use the police as sentinels such as hot spots policing are particularly effective.
Retribution this philosophy is the belief that those who commit criminal acts should be punished according to the seriousness of the crime and that no other circumstances are considered deterrence this strategy is the thought that if the. Punishment after all has worked for us. Some authors have argued that the purpose of punishment is to give satisfaction to the victim in the sense that it makes the victim feel better.
4 It must be administered intentionally by someone other than the offender. Most states in the US. Even when the purposes are valid punishment may be limited by moral values or practical concerns.
For punishment to reduce future crimes the pain and unhappiness caused to the offender must be outweighed by the avoidance of unpleasantness to other people in the future Cavadino 2002. It prevents future crime by disabling or restricting the offenders liberty their movements or ability to commit a further wrong. Punishment purposes are positive justifying principles.

Sociology Social Science Research Methods
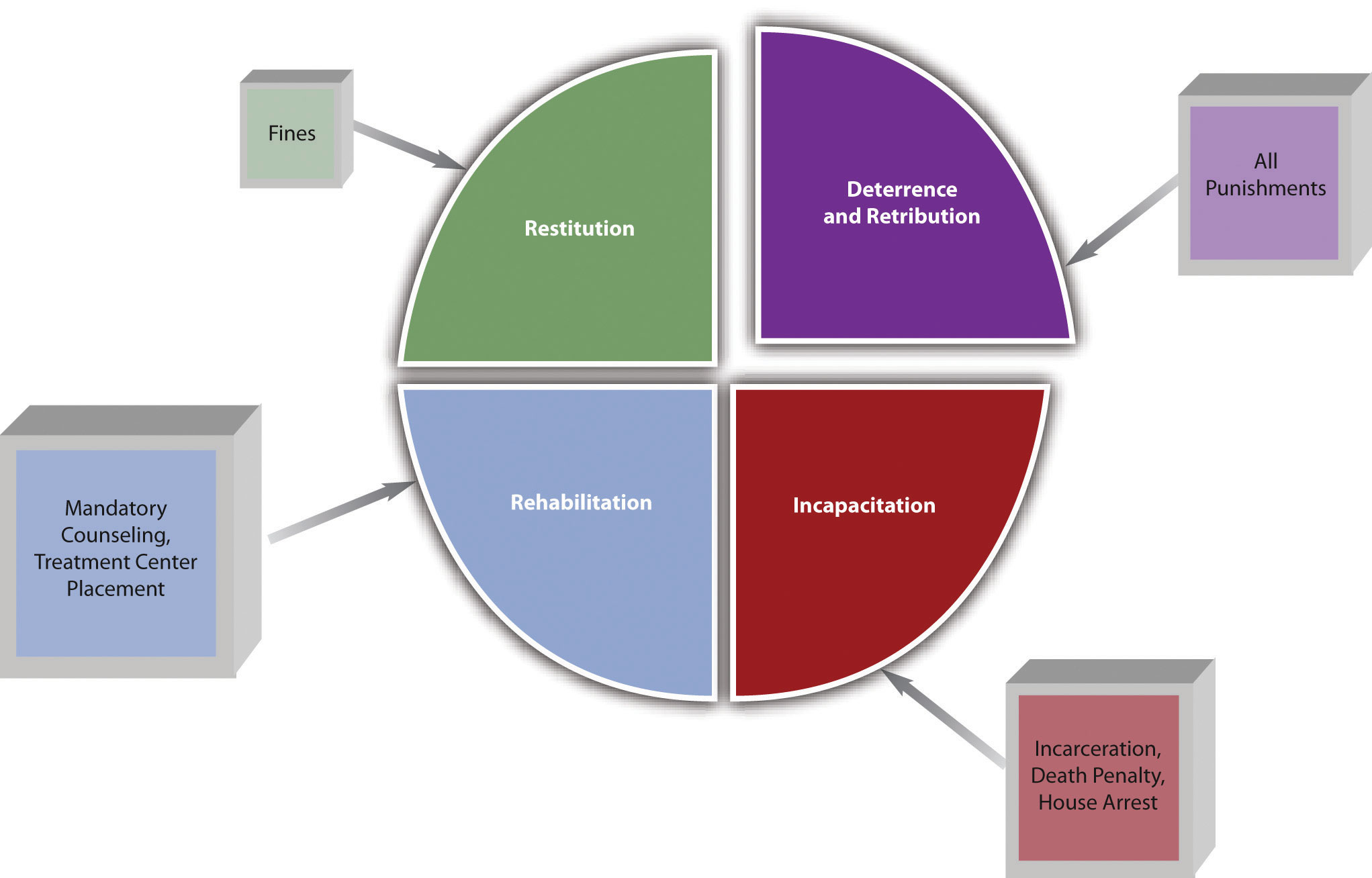
1 5 The Purposes Of Punishment Criminal Law

Applied Behavior Analysis Applied Behavior Analysis Behavior Analysis Aba Therapy Activities
Comments
Post a Comment